ABM COMPOSITE OY’S ARCBIOX™ MFAs ARE READY TO MEET YOUR DISHWASHERS
Published: 21/09/2020
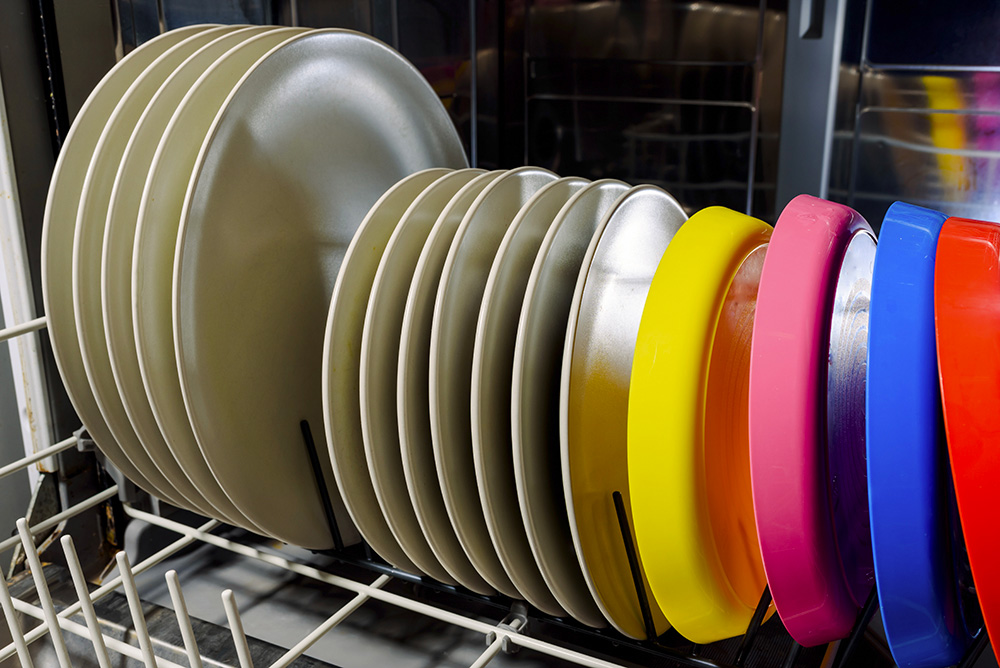

Many fast food products, sold for outside use during a work break, or a trip (for example green salads, couscous, rice salads, etc …), are presented in rigid packaging (trays), accompanied by condiments and plastic cutlery. The latter are part of the so-called disposable products which have recently undergone restrictions by the legislator, who has assimilated them to a powerful weapon of pollution of the Planet. Often and unfortunately due to ignorance, or neglect, on the consumer’s part.
On the European front, the directives have long been pushing towards circularity (Circular Economy).
To reduce the environmental impact, the EU has fielded funds and guidelines under the prefix “Re”: Re-cycling, Re-use, Re-pair.
To reduce environmental impact, in terms of CO2 content, the optimal conditions are certainly recycling, reuse or repair of the product at the end of its life. Unfortunately, however, recycling, as it is still implemented today in much of the world, shows an uncertain “end of life” for plastics, also due to the heterogeneity of these materials. The overall numbers of true recycling remain low (less than 40%) and show that at best, the end of life for them is called thermal recovering (burning). In the worst cases, unfortunately still current, it is called landfill. This ends up weighing heavily on the LCA of the artifact.
The advantages of reuse
The reuse of plastic products where possible is a very interesting solution. It allows to obtain two goals, the reduction of the need for virgin raw materials and, gradually, to reduce (from the second use onward) the total weight of CO2 up to about 80%.
Obviously, in order for the product to be reused, this must be able to count on a material capable of adequately withstanding working temperatures, contact with food without releasing critical chemicals and, also important, maintaining its original properties even being washed a certain number of times, by hand and/or in the dishwasher.
Moreover, if at the end of its useful life the artifact is transformed into compost, then the life cycle becomes truly virtuous from the cradle to the grave.
ABM Composite is ready to support this virtuous practice. It has developed a family of Biobased technical and specific products for that: the ArcBiox™ MFAs.
These are materials capable of providing performance suitable for the production of single-multi-use tableware, capable of satisfying the application needs of food bowls and tableware.
The ArcBiox™ MFAs main features are:
- thermal resistance => 80 ° C
- excellent mechanical rigidity
- excellent processability in existing moulds
- low volumetric shrinkage
- excellent surface quality
- rapid processing cycles (molds at 30°C)
- suitability for food contact (European legislation)
- compostability at the end of life (industrial compost – EU 13432)
- absence of smell and taste
- excellent resistance to repeated washing, even in dishwashers
ArcBiox™ MFAs are an opportunity also for designers who want to deal with this new virtuous trend, which will certainly be able to derive advantages and added value from their creativity.
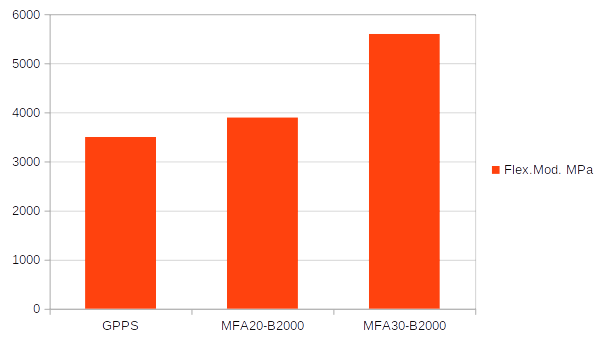
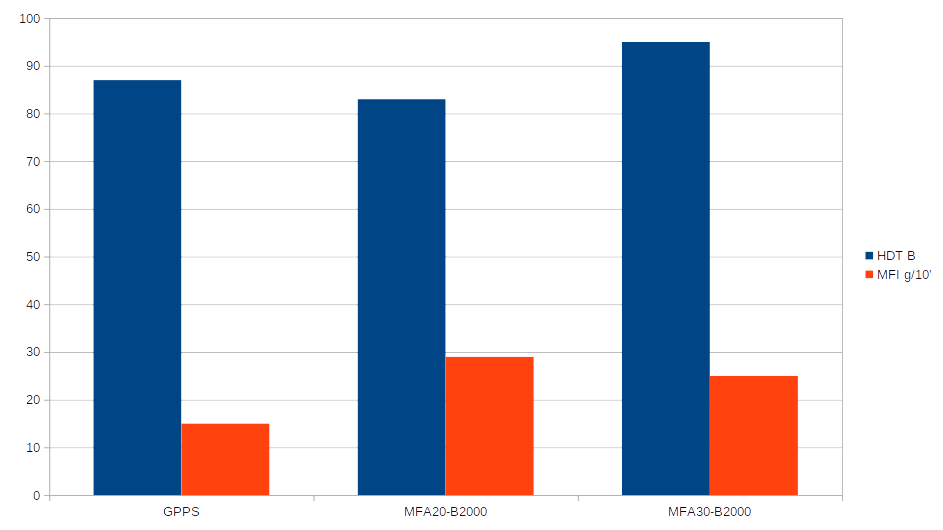
Technical properties comparison GPPS (General Pourpose PS) and ArcBiox™ MFA20 and 30-B2000.
1)Flexural Modulus at 23°C
2) Heat Distortion Temperature (HDT B °C) and Melt Flow Index (grams/10 minutes)
To find out more about the compostable grades available and their applicability instead of fossil products, send an email to: info@2milasrl.it or call us on +39.3245969132.
Share the article on your favorite social:
Did you find the article interesting?


Are there any topics you'd like to see covered in this blog?
Your comments and requests are important to us: write them in the space below, it's available to you!